March 26, 2025
Development of a Key Component for Laser FusionThe Glass Faraday Element: A Crucial Innovation for Large High-Power Lasers
Research Results (Press Release)Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd. (Head Office: Otsu, Shiga, Japan; President: Akira Kishimoto), Institute of Laser Engineering at Osaka University, National Institute of Fusion Science, and Kyoto University have developed "Glass Faraday Element" as key component of large high-power lasers. The optical isolator incorporating this component suppresses reflected return light, a major issue in large high-power lasers. High-power lasers are expected to find applications in a variety of fields that require precision engineering and advanced laser control, such as laser fusion, the removal of space debris, and cancer therapy using heavy particle beams.
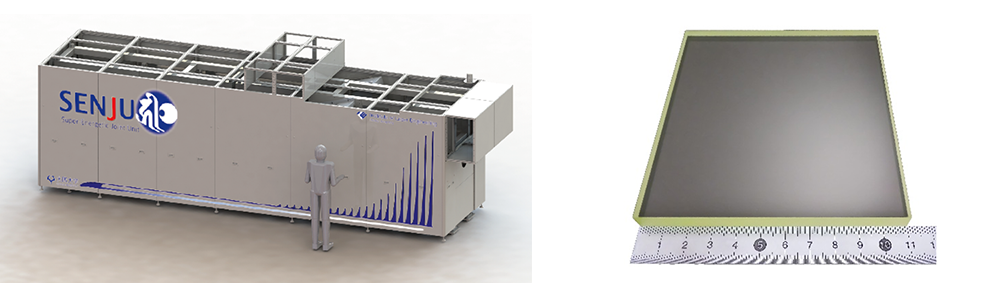
Right: Developed glass-made faraday device 110×110mm
Institute of Laser Engineering at Osaka University is currently developing a large-scale high-power laser system called SENJU, which features a large beam diameter of Φ90mm. As a key part for controlling the beam, Glass Faraday Element that can be made large in size are considered promising.
Features of Glass Faraday Element
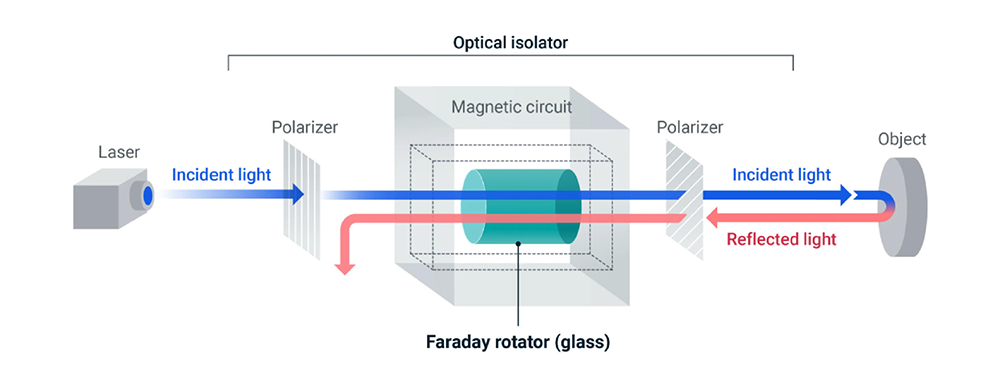
The Glass Faraday Element is an optical component used in optical isolators. It is a specialized device that utilizes a magnetic field to rotate the plane of polarization of light. The newly developed glass-made faraday device has the following features, surpassing conventional materials such as terbium gallium garnet (TGG).
- Can be manufactured in larger sizes
It is 110×110mm enough to control very large diameter beams (Φ90mm). - High-power resistance
With a lower absorption coefficient than TGG, it maintains optical integrity even under high-power laser operation.
Background of joint development
Reflected return light from high-power lasers poses a major challenge for the realization of the equipment, as it poses a risk of laser equipment damage and noise problems. Nippon Electric Glass has developed a glass-made faraday element that meets the requirements for large, high-power lasers by leveraging its experience in developing compact high-power (high-power) laser-compatible optical isolators. Kyoto University and the National Institute of Fusion Science are evaluating the glass. The Institute of Laser Engineering at Osaka University is implementing it as an optical isolator for the "SENJU".
Future prospects
We will continue prototyping glass with suitable size and thickness for laser fusion, while evaluating its optical properties and performance. We are advancing toward the commercialization of an optical isolator incorporating the Glass Faraday Element.
